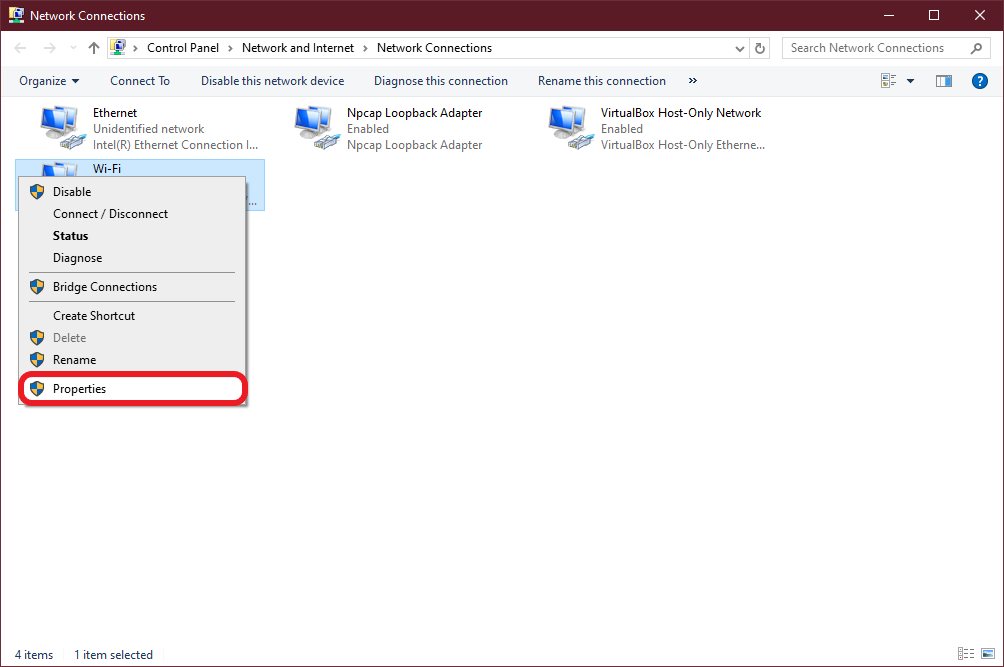
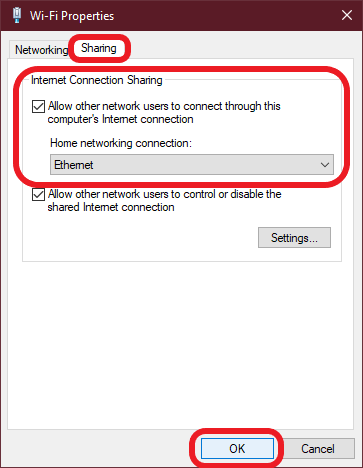
The goal of this story is to give a brief introduction into the OSI Model and a helpful way to remember the different layers. Not everything translates nicely into a story format.
Disclaimer: Some of the concepts are simplified. If you have any suggestions or issues, feel free to drop a comment below.
Once upon a time. In a lan far far away. A young boy was walking along a dusty path with his teacher, the old wise wizard of ARPANET. So Arthur, for that was the name of our young boy, how is your learning of the OSI model coming? Truth be told master, I am having the hardest time keeping things straight, and even understanding what a Network Model is. Why are there so many layers and remembering if the presentation comes before the transport, or transport before presentation. It is all very confusing. The old wizard nodded, ah yes, it can be a bit of a muddle and the OSI model is not even the primary model used, but alas, it is a relic that is still taught and expected of students in your order. Fortunately, we have just stumbled upon a great example that may help. They had just arrived at a building that was in the middle of nowhere, but appeared to be heavily guarded. Arthur had not been here before and was not sure what to make of it. The wizard continued, this is one of the kings mines and it looks like they are just about to send off some gold over the Internet.
Sit here on this rock and let’s review what the OSI model is. The OSI Model stands for Open Systems Interconnection is a network model developed by the ISO or International Organization of Standardization. The model is a theoretical model of how a network can send and receive data. Technically, applications can be built on top of this model. However this model has been largely abandoned in favor of TCP/IP. There are some similarities and the OSI model is still taught and referenced, but TCP/IP is simpler and is what people preferred. For instance when someone says “that is a layer 7 problem”, they are referring to the Application layer. But now let us get into the layers. Look, they are loading up the gold.
You see the road there that runs in front of the mine? We can compare the road to the first layer of the OSI model, the Physical Layer. The physical layer is well, the physical medium that is used. There are multiple mediums that could be used. Roads are one, rivers another, we can even use the air wirelessly. There are also more esoteric paths like Fiber and Cable.
The next layer is our cart. This is commonly referred to as layer 2 and has everything to do with switching and MAC addresses.
A cart is useless without a driver, and that is the next layer. Our driver and the routing to the treasury is our Network Layer, layer 3. He follows the IP routes from here to there. The signs help route between road networks so he can get to the destination.
You see the boxes that are being loaded? That is Layer 4. The Transport Layer. We typically have two types of transport TCP and UDP. TCP is in closed boxes that keep the contents from bouncing out while going down the road, there are also mechanisms in place to verify that everything gets to the destination and if something is missing, it will make sure to go back and get it. UDP is a simpler protocol. See that cart over there under the apple tree? They just throw all the apples in and hope it all makes it to the destination. There is no verification that it makes it to the destination, they just send it and hope for the best or handle the errors at a higher layer. It is a simpler protocol and faster. And honestly, if a load of apples goes missing, it is not the end of the world.
Now on the journey, the driver is going to need to be let through the gates into the treasury. We can thinks of the guards and gates as our Session Layer or Layer 5. They initiate the session and will tear it down, close the gates, once the load is delivered.
The presentation layer is next, and it is responsible for converting data from one format to another. Things like formatting, encryption and compression are all executed in this layer. For instance, if the load was a bunch of feathers, it could be compressed down to fit a higher quantity of feathers in the same size cart. In this case, the presentation layer is responsible for encrypting, or locking the box. When it gets to its destination, it will be unlocked so it can be accessed.
Finally, Layer 7. The Application Layer can be thought of as the end user interface. In this case the actual gold coins. We can handle it, look at it, and count them.
That is the OSI layer in a nutshell. It is important to remember that it is only a theoretical framework and not exactly how everything works. There are some protocols that have been built on the OSI model, but most of the Internet uses the TCP/IP model.
Arthur sighed, that is a lot to take in, but having the visual will be helpful. Is there a mnemonic or jingle to help remember the names? Aye, we’ve a few, the old wizard replied smiling. One that has been around for ages is, All People Seem To Need Data Processing. Or you can start at the physical layer and go up with, Please Do Not Throw Sausage Pizza Away. Arthur laughed, why would someone throw sausage pizza away? They both chuckled. Hopefully no one does that Wizard said. Now up, let’s see if we can catch the cart so we can continue our learning.