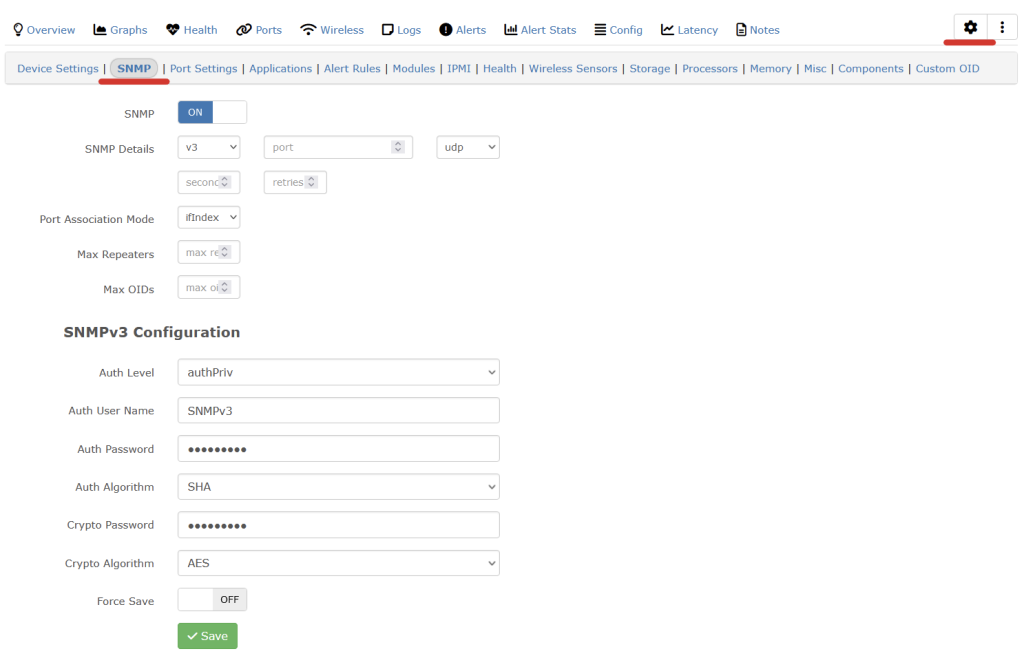
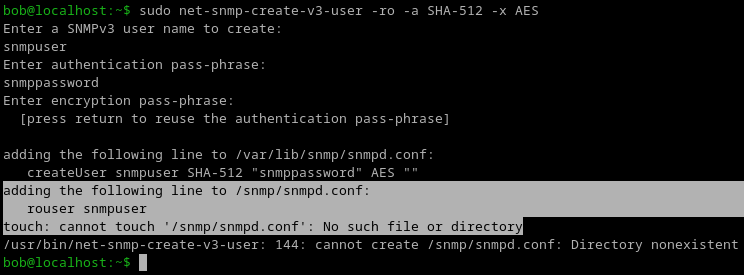
The following works for setting the snmpv3 configuration on cambium 450i 900’s. Once applied it’ll run change the SNMP settings and reboot the radio.
You’ll need to find the hashed password which can be found in a config backup.
Change the SNMP username/community as needed.
{
"userParameters": {
"snmpConfig": {
"user2Group": 0,
"snmpv3EngineId": "007000a9840a003e464e7a",
"rwAuthPasswordEncrypted": "3e5h24a694a515e81abb6b25986cea91",
"commStringROnly": "rocommunitystring2",
"user2PrivPassword": "",
"user1AuthPassword": "",
"snmpv3AuthProt": 0,
"snmpv3TrapEnable": 0,
"snmpv3PrivProt": 0,
"snmpMibPerm": 1,
"roAuthPasswordEncrypted": "3e5h24a694a515e81abb6b25986cea91",
"commStringRW": "communitystring",
"userGroup1": 0,
"user1Enable": 0,
"snmpv3SecLvl": 2,
"user2Enable": 0,
"rwUserName": "Canopy",
"roUserName": "snmpv3user",
"roPrivPasswordEncrypted": "3e5h24a694a515e81abb6b25986cea91",
"userName1": "",
"snmpPort": 161,
"rwUserEnable": 0,
"trapDomainNameAppend": 0,
"rwPrivPasswordEncrypted": "3e5h24a694a515e81abb6b25986cea91",
"user1PrivPassword": "",
"userName2": "",
"user3PrivPassword": "",
"user2AuthPassword": "",
"userName3": "",
"user3Enable": 0,
"snmpTrapPort": 162,
"user3AuthPassword": "",
"user3Group": 0,
"trapDelayAfterBootup": 5,
"snmpIpAccessFilter": [
{
"address": "192.168.0.0",
"netmask": 24
},
{
"address": "10.0.1.0",
"netmask": 24
},
{
"address": "0.0.0.0",
"netmask": 0
},
{
"address": "0.0.0.0",
"netmask": 0
},
{
"address": "0.0.0.0",
"netmask": 0
},
{
"address": "0.0.0.0",
"netmask": 0
},
{
"address": "0.0.0.0",
"netmask": 0
},
{
"address": "0.0.0.0",
"netmask": 0
},
{
"address": "0.0.0.0",
"netmask": 0
},
{
"address": "0.0.0.0",
"netmask": 0
}
],
"snmpTrapAddresses": [
"0.0.0.0",
"0.0.0.0",
"0.0.0.0",
"0.0.0.0",
"0.0.0.0",
"0.0.0.0",
"0.0.0.0",
"0.0.0.0",
"0.0.0.0",
"0.0.0.0"
]
},
}